Code Bias in the Beauty Industry: Examining Facial Recognition and Skincare Finders
The beauty industry has embraced technological advancements, including facial recognition technology and AI-driven skincare finders, to provide personalized recommendations to consumers. However, concerns have been raised regarding code bias within these technologies, particularly in relation to promoting racial stereotypes and accuracy on darker skin tones. In this article, we will be testing 4 different skin tones in 2 different facial recognition solutions from NYX, Vichy, and No7, in order to test for a bias by looking at the results from each
KEY:
Estella, fair skin: Dry skin, concerns include hydration, sun protection fine lines, and wrinkles.
Shauneez, brown skin: Combination skin, skin concerns are hyperpigmentation, sun protection, and dark spots
Jessica, deep brown: Combination skin with skin concerns of lack of radiance
Aby, dark skin: Oil with skin concerns of hyperpigmentation and pore visibility
Facial Recognition and Code Bias:
Facial recognition technology identifies and classifies human faces based on various facial features. Using machine learning algorithms, face detection software detects faces by identifying facial features in a photo or video. It first looks for an eye, and from there, it identifies other facial features. It then compares these features to training data to confirm it has detected a face. However, CODED BIAS a movie by MIT Media Lab researcher Joy Buolamwini explores the discovery that facial recognition does not see dark-skinned faces accurately. The lack of diversity in training datasets contributes to this code bias, as most datasets primarily consist of lighter skin tones. Consequently, facial recognition technology may perpetuate racial stereotypes and inaccuracies when applied in the skincare industry.
Facial Recognition and Accuracy on Lighter Skin:
Facial recognition is used by skincare brands to recommend products based on a user's skin type, concerns, and preferences. However, the accuracy of these tools on lighter skin tones may be higher due to the limited representation of darker skin tones in the datasets used for training. As a result, skincare finders through facial recognition may provide more accurate recommendations for individuals with lighter skin, while potentially neglecting the specific needs of those with darker skin.
Examining Test Results:
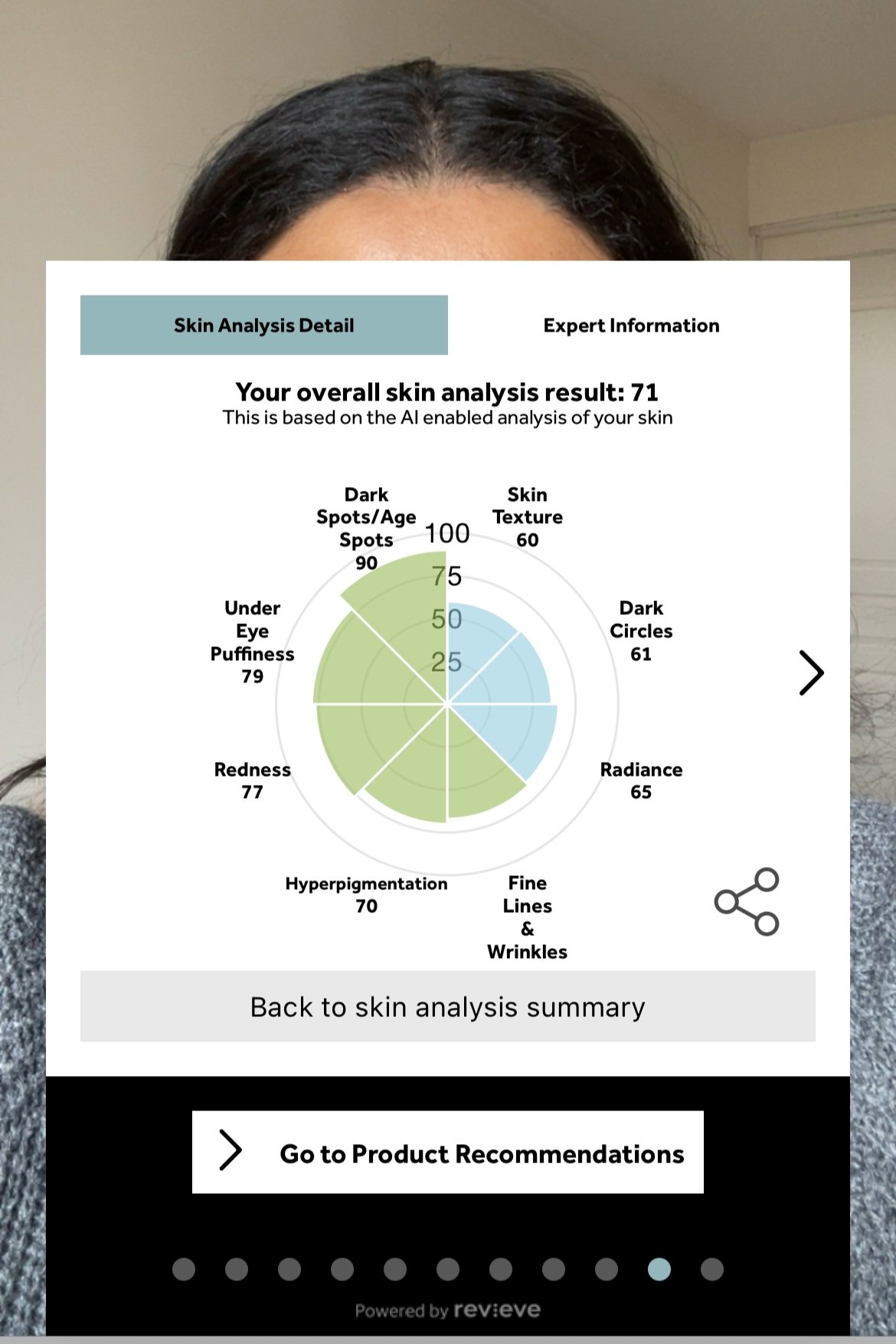
Vichy SkinConsult AI
The Vichy SkinConsult facial recognition is aimed to identify participants' skin types and concerns and provide personalized product recommendations. The results for each skin tone are as follows:
Estella: Her prediction is that she has dry skin, which was verified by asking her which skin type she has, the final result from Estella: “Even though the analysis summary at the end did not capture my needs fully, the products I got recommended were on point.”
Shauneez: Combination skin with concerns of hyperpigmentation and dark spots. The final result from Shauneez: “I actually had no problem with this skin test, it seemed pretty accurate and the product was great”
Aby: Oily skin, with skin concerns of lack of radiance and pore visibility. The final result from Aby: “The test was pretty easy and fast. Maybe they can ask for pictures of the sides of the face because in my case, it's where I have the most hyperpigmentation”
Jessica: Combination skin with skin concerns of lack of radiance and dark spots. The final result from Jessica: “Overall, the test was good. Straight forward and clear next steps. I would only like for it to detect my skin type to ensure as much accuracy as possible.”
Overall conclusion:
This skin test didn’t actually do much, the customers have to tell it what skin type they have and then they get their products. While participants generally found the recommended products suitable for their needs, there were instances where the analysis seemed off or failed to capture certain concerns accurately. This indicates potential limitations in accurately assessing individuals with darker skin tones and specific skin concerns, such as hyperpigmentation and deep wrinkles.
Test Results:
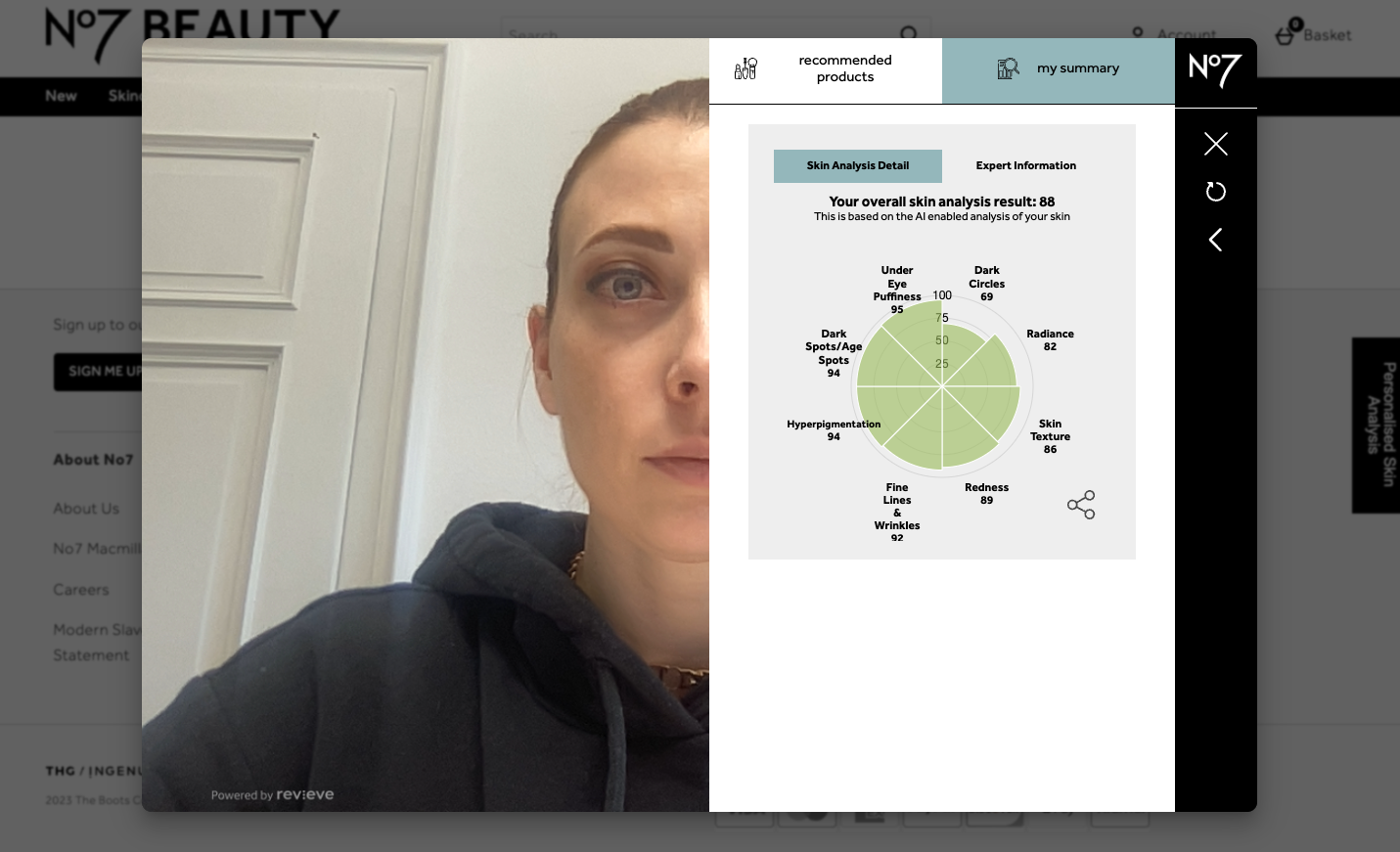
No7 Skincare
The No7 test also employed facial recognition to determine skin type and concerns for personalized product recommendations. When asked did these products address your skin needs the results are as follows:
Estella: “Results were exactly what I have selected in the quiz previously of the facial scanning. There did not seem to be any detection of needs.”
Shauneez: “Same experience, the solution recommends what we have asked for, nothing new detected or learned.”
Jessica: “The products offered were products that I think were passed on my quiz entry and not the assessment. I have less faith in this as the only concern I believe that I did not select was fine lines/wrinkles and when I looked at my results there was no score for fine lines/wrinkles.”
Aby: “The products address my skin needs but they might not be enough to tackle my hyperpigmentation issues”
Overall conclusion:
Participants noted that the recommendations aligned with their input during the quiz stage rather than the facial analysis. This suggests a reliance on user-provided information rather than leveraging true facial recognition technology.
Conclusion:
It seemed that the common issue of facial recognition was hyperpigmentation. According to the National Library of Medicine, hyperpigmentation occurs more often in darker skin tones due to there being more melanin. This could indicate a bias as all 3 participants with darker skin had hyperpigmentation concerns that were either not picked up or treated correctly. Code bias in the beauty industry, particularly in facial recognition and skincare finders, poses challenges in accurately assessing and recommending skincare products for individuals with darker skin tones.
Disclaimer: Even though this was not a statistically relevant test and we have only used 4 people who experienced inaccuracies, the need for additional data input, and the lack of trust of the users were evaluated in this qualitative research.
Data-Driven Recommendations
Skin Match Technology uses a quiz-based product finder to provide inclusive, individual, and accurate recommendations. 82% of people buying a product are happy with it. Customers trust the result because we are delivering an explanation and the recommendation is based on 60K Ingredients, Product Details, and the individual needs of each unique user.
All about the Skin Match Technology Data Driven Foundation and Shade Finder
-
-Our Database covers 112 Different Skin Tones
-10’000 Products in the following Categories
65% Foundations
19% Concealers
5% Tinted Moisturizers
5% Face Powders
Companies like IT Cosmetics and Giorgio Armani are achieving up to a +30% increase in conversions with it.
-
Step 1: Color matching, we take a look at your inventory
Step 2: Make it your own, we customize it for brand and preferences
Step 3: Plug & play ,No developer is required for our standard integration.
Step 4, Unlock insights, Access your analytics dashboard for insights into best-performing products, click-through rate and matched products.
If you have inventory changes, talk to your project manager to get them updated.
-
-Beauty retailers that offer multiple brands with a wide range of skin tones for foundations, BB/CC Creams, powders and/or concealers from light to dark, this is for you.
-Beauty brands that offer a wide range of products like BB/CC creams, foundations, powders, and/or concealers from light to dark to build your best base, this is also for you!